 Botswana Telecommunications Corporation (BTC)
Botswana Telecommunications Corporation (BTC)
All data are collected in the Fiscal Year of 2008-2009.
Company Profile and History
BTC was established in 1980 to provide, develop, operate and manage Botswana's national and international telecommunications services. In 1996, an amendment of the BTC Act repealed the monopoly of BTC and introduced indirect competition through two cellular joint venture consortiums, Mascom Wireless and Vista Communications (now Orange). The Act further established a regulatory authority and liberalised the market with particular emphasis on customer premises equipment and value added services, many of which are now in full competition to BTC.
BTC has two regional offices, four districts offices and a number of customer care centres to cater for service delivery nationally. It also publishes the Botswana Telephone Directory and provides a countrywide directory assistance services. BTC’s is run by a Board, appointed in terms of the BTC Act, supported by an Executive Management Committee.
In Country Location
Megaleng Khama Crescent, Plot 50350, Gaborone, Botswana;
Telephone: +3958000
Services and Products
BTC’s core business has been voice and data services through a broad spectrum of modern network platforms until recently, when the Cooperation started provision of mobile services. In 2008, BTC commenced a mobile telephony service under the brand name beMobile.
The Corporation’s range of communications products and services include wired and wireless networks, basic voice telephony and voice messaging, Internet Protocol (IP) based networks and solutions, high speed Internet access, data networks, customer premises equipment (PABXs), optical fibre connectivity solutions and online directory services. The Corporation's range of services is built around its national networks comprising wired and wireless connections.
The introduction of basic rate Integrated Services Digital Networks (ISDN) was undertaken to address the growing telecommunications requirements especially in the business sector. BTC also offers value added services in addition to basic telephony. These include; call diversion and forwarding, three party conferencing, abbreviated dialling, call waiting, international and national call barring, alarm call, 0800 toll free services and voice messaging.
Data communications services by BTC are available through a managed data network on a point to point and point – to a multi point that can be provided to customers at their bandwidth requirements. These services are Frame Relay (BotsFrame), leased lines and ATM. The Corporation also provides high capacity access to Internet for major corporate customers and Internet Service providers (ISPs). Points of presence (POPS) are now established in five centres around the country enabling Internet customers to dial at the cost of a local call.
Number of Employees
1,057 people
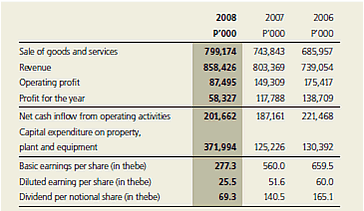
Financial Information
Market Share
Currently BTC is the only fixed line operator in Botswana. beMobile is the third largest cellco of Botswana in terms of subscribers
Business Objective
“To be the communications company of choice-focused on delivering exceptional value to our customers, employees and shareholders”
Business Model
BTC plans to achieve its business goals through various strategies, including: maintaining up-to-date technology in the implementation of services; maintaining and enhancing relationships with customers; increase revenue volumes from existing and new products and decrease costs to offset the anticipated declines in telecommunications tariffs; and leveraging its leadership in a converged fixed mobile networks in three growth areas: voice, data and internet. New services will focus on fixed/wireless/mobile/internet convergence, as well as virtual private networks and advanced data services.
Ownership of Business
BTC is a parastatal in which the Botswana government holds 100% equity.
Benefits Offered and Relations with Government
BTC is to be privatised. So far the dead line has not been met owing to some procedural delays. The method suggested for privatisation includes a selection of a suitable Strategic Equity Partner (SEP) up to the limit of 49% of the controlling interest. The privatisation also includes share offerings under an Employee Share Option Plan under which they will be able to obtain up to 5% of the share offer.
Privatisation of BTC will result in taxation on BTC’s future profits and this will have a significant impact on the profitability and the free cashflow available for the Corporation.
Botswana’s National Information and Communications Technology (ICT) vision through it’s “Maitlamo” initiatives aim to make Botswana a globally competitive, knowledge and information society where lasting improvements in social, economic and cultural development is achieved through effective use of ICT by 2016. The Government of Botswana planned to achieve these through: creation of an enabling environment for the growth of an ICT industry in the country; provision of universal service and access to information and communication facilities in the country; and making Botswana a Regional ICT hub so as to make the country’s ICT sector globally competitive.
Realising that the liberalisation of the telecommunications sector has still not benefited the bulk of the population in Botswana, the Government of Botswana has taken two major steps in bringing telecommunications services to all parts of Botswana: issuing of three Public Telecommunications Operator licences, which will enable the three operators to provide virtually any type of telecommunications services within allocated spectrum resources; and opening up the provision of services in the rural areas under a separate arrangement by a tendering process.
BTC has committed itself to support the initiatives, in collaboration with the Government, through the provision of an enabling network environment to connect communities, businesses, residential homes, Government offices, schools, hospitals and clinics etc. anywhere in country.
Product Development
The privatisation process gathered momentum during 2008 with the appointment of a transaction advisor by the Public Enterprises and Privatisation Agency (PEEPA), the Government arm for privatization initiatives.
beMobile, BTC’s mobile arm came into operation in April 2008. The network which currently works on a 2.5G technology through Global System for Mobile (GSM) network will be upgraded to 3G technology capable of transmitting high speed data for most parts of the country.
Most secondary schools throughout the country have been connected with a broadband (ADSL) network coupled with internet services as part of the SchoolNet project. Further, plans are also in the pipeline to connect primary schools to broadband in the near future. This would be inline Vision 2016. Through the Nteletsa Project a number of rural villages which did not have communications have been brought into service




