Ecobank Malawi
Ecobank Malawi
All data are collected in the Fiscal Year of 2008-2009.
Company Profile and History
Ecobank is a full-service bank providing a broad range of products and services to governments, financial institutions, multinationals, international organisations, medium, small and micro businesses and individuals. Listed on three stock exchanges, Ecobank is also the leading pan-African bank with operations in 27 countries across the continent.
Ecobank Transnational Incorporated (ETI), a public limited liability company, was established as a bank holding company in 1985 under a private sector initiative spearheaded by the Federation of West African Chambers of Commerce and Industry with the support of ECOWAS.
[ Note: In the early 1980s the banking industry in West Africa was dominated by foreign and state-owned banks. There were hardly any commercial banks in West Africa owned and managed by the African private sector. ETI was founded with the objective of filling this vacuum. ]
In October 1985, ETI was incorporated with an authorised capital of US$100 million. The initial paid up capital of ETI of US$32 million was raised from over 1 500 individuals and institutions from West African countries. The largest shareholder was the ECOWAS Fund for Cooperation, Compensation and Development (ECOWAS Fund), the development finance arm of the ECOWAS.
ETI commenced operations with its first subsidiary in Togo in March 1988. Today, the Ecobank Group is a full-service regional banking institution employing over 11 000 staff in over 600 branches and offices in twenty seven (27) west, central and east and southern African countries namely Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cape Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo Brazzaville, Democratic Republic of Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Gabon, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome & Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo.
ETI has two specialised subsidiaries: Ecobank Development Corporation (EDC) and eProcess International (eProcess). EDC was incorporated with a broad mandate to develop Ecobank’s investment banking and advisory businesses throughout the countries where Ecobank operates. EDC operates brokerage houses on all 3 stock exchanges in West Africa and has obtained licences to operate on the 2 stock exchanges in Central Africa: the Douala Stock Exchange in Cameroon and the Libreville Exchange in Gabon. The mandate of eProcess is to manage the Group’s information technology function with a view to ultimately centralising the Group’s middle and back office operations to improve efficiency, service standards and reduce costs.
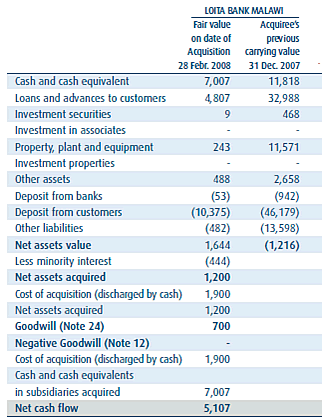
In February 2008, the group acquired 73 percent of the share capital of Loita Bank of Malawi and the bank was renamed EcoBank Malawi.
In Country Location
Loita House, Corner Victoria Avenue & Henderson Street, Chichiri, Blantyre 3 – Malawi; Phone: (265) 01 822 808 / 099; Fax: (265) 01 822 683 / 820 583
Services and Products
In addition to the traditional banking products and services, Ecobank offers products and services including Internet Banking, Telephone Banking, and Ecobank Regional Cards.
Number of Employees
49 employees
Financial Information
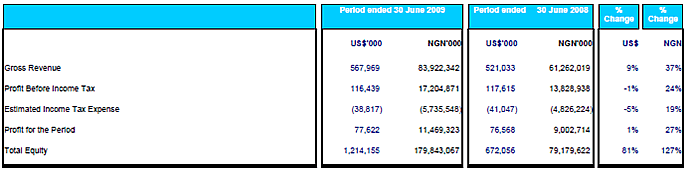
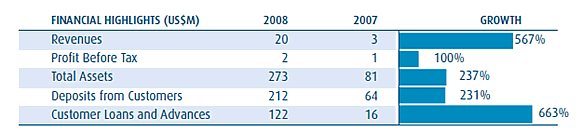
The acquired bank (Loita) contributed operating income and profit before tax of US$2,9 million and US$0,1 million respectively to the group for the period from 1 March 2008 to 31 December 2008. If the acquisition had occurred on 1 January 2008, the contribution to the group operating income and profit before allocations would have been US$3,3 million and US$0,3 million respectively
Market Share
Ecobank Malawi has an approximate 5 percent market share
Business Objective
“To build a world-class African bank and to contribute to the economic and financial integration and development of the African continent”
Business Model
“As a group, our strategy is to build scale through organic growth and acquisitions, and also grow our businesses in existing markets and expand into new markets.
Scale: We continue to explore new ways of increasing our reach through the use of alternative channels such as alliances and sales agents.
Growth: While Ecobank has thus far witnessed a period of sustained growth, the markets in which we operate experienced a downturn due to the global economic slowdown, which affected our growth. In addition, Ecobank’s regional expansion strategy is coming to an end with only a few countries left to cover. Ecobank’s growth strategy will increasingly take advantage of some of the immense opportunities that abound in our markets, such as a large under-banked population, opportunities in mobile, transaction and consumer banking, and in facilitating cross border trade and payments.
Efficiency: As a result of our continued expansion, we experienced some deterioration in our efficiency ratios. The ratio of non-performing loans (NPLs) deteriorated from 6% to 8%. In view of the expensive but weak technology and telecommunications infrastructure in Africa, we shall continue to refine our technology model to reduce costs by ensuring an appropriate balance of activities that can be centralized, regionalized and localized.
Ecobank operates as "One Bank" with a common brand and common standards, policies and processes. With our geographical expansion coming to an end, we shall focus increasingly on improving controls, customer service, processes, efficiency, productivity and using technology to leverage our unparalleled presence across Africa.”
Ownership of Business
Ecobank Malawi Limited is a subsidiary of Ecobank Transnational Incorporated (ETI).
Benefits Offered and Relations with Government
The Reserve Bank of Malawi is the regulator of financial services and provider of settlement services in the country. The central bank also assumes a supervisory role over the country’s payment systems. The Bank is also a participant in the payment system and therefore also fulfils the role of a settlement bank.
According to the United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF), the Government of Malawi has taken steps to improve the climate for a viable financial industry. These steps include liberalizing the sector, reducing interest rate controls, lowering bank reserves, and removing exchange regulations on capital flows. The Government has also taken steps to improve the regulatory framework to attract private investors. The Companies Act and the Capital Market Development Act are examples of functioning regulatory structures set in place to promote investment in Malawi. Financial sector reforms have resulted in the entry of several international financial institutions into the banking sector.
Moreover, the Government has shown substantial flexibility in relaxing equity-ownership rules for the banking industry: foreign banks are allowed to own a 100 percent stake in their Malawian counterparts.
Product Development
Ecobank has indicated that it is considering launching its own mortgage and/or home improvement products in the near future.